ZooKeeper介绍 ZooKeeper是一个分布式协调服务、分布式数据一致性的解决方案,是Google Chubby的开源实现。分布式应用程序可以基于它实现诸如发布/订阅、负载均衡、命名服务、分布式协调/通知、集群管理、Master选举、分布式锁和分布式队列等功能。
ZooKeeper分布式特性 顺序一致性:从同一个客户端发起的事务请求,最终将会严格地按照其发起顺序被应用到ZooKeeper中去。
原子性:所有事务请求的处理结果在整个集群中所有机器上的应用情况是一致的,即要么整个集群所有机器都成功应用了某一个事务,要么都没有应用。
单一视图:无论客户端连接的是哪个ZooKeeper服务器,其看到的服务端数据模型都是一致的。
可靠性:一旦服务端成功地应用了一个事务,并完成对客户端的响应,那么该事务所引用的服务端状态变更将会被一直保留下来,除非又另一个事务又对其进行了变更。
实时性:一旦一个事务被成功应用,那么客户端能够被立即从服务端上读取到这个事务变更后的最新数据状态。但ZooKeeper仅仅保证在一定的时间段内,客户端最终一定能够从服务端上读取到最新的数据状态。
ZooKeeper设计目标 ZooKeeper致力于提供一个高性能、高可用,且最具有严格的顺序访问控制能力(主要写操作的严格顺序性)的分布式协调服务。
(1)简单的数据模型
ZooKeeper使得分布式程序能够通过一个共享的、树型结构的命名空间来进行享互协调。树型结构的名字空间是指ZooKeeper服务器内存中的一个数据模型,其由一些列被称为ZNode的数据节点组成,类似文件系统。不同之处在ZooKeeper将全部数据存储在内存中,以此来实现提高服务器吞吐、减少延迟。
(2)可以构建集群
ZooKeeper由一组机器组成,可以3~5台机器,建议不小于3的奇数。
组成ZooKeeper集群的每台服务器都会在内存中维护当前的服务器状态,并且每台机子之间都互相保持着通信。只要集群中保持着一般的机子能够正常工作,那么整个集群九能够正常对外服务。
ZooKeeper的客服端程序会选择和集群中任意一台机器共同创建一个TCP连接,而一旦客户端和某台ZooKeeper服务之间的连接断开后,客服端会自动连接到集群中的其它机器。
(3)顺序访问
对于来自客户端的每个更新请求,ZooKeeper都会分配一个全局唯一的递增编号,这个编号反映了所有事务操作的时候顺序,应用程序可以使用ZooKeeper的这个特性来实现更高层次的同步原语。
(4)高性能
由于ZooKeeper将全部数据存储在内存中,并直接服务与客户端的所有非事务请求,因此尤其适用于以读操作为主的应用场景。
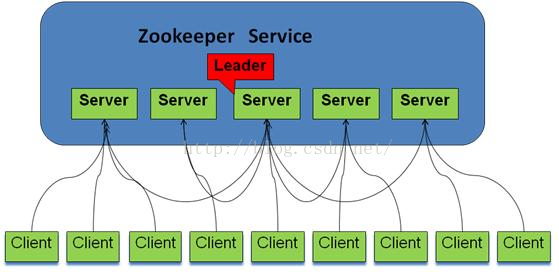
ZooKeeper基本概念 集群 ZooKeeper并没有沿用传统的Master/Slave模式,而是引入Leader、Follower和Observer三种角色。ZooKeeper集群中的所有机器通过一个Leader选举过程来选定一台被称为“Leader”的机器,Leader服务器为客户端提供读和写的服务。Follower和Observer都能够提供读服务,唯一的区别在于Observer机器不参与Leader选举过程,也不参与写操作的“过半写成功”策略,因此Observer在不影响写性能的情况下提升集群的读性能。
会话 https://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/p/6103870.html
数据节点(Znode) 分布式中,“节点”指组成集群的每一台机器。在ZooKeeper中,“节点”分为两类,第一类指构成集群的机器,称为机器节点;第二类指数据模型中的数据单元,称为数据节点(ZNode)。
ZooKeeper将所有的数据存储在内存中,数据模型是一棵树(ZNode Tree)。名字空间由节点znode构成,其组织方式类似文件系统,其中各个节点相当于目录和文件,通过路径作为唯一标识,例如/path1/path2。
与文件系统不同的是,每个节点具有与之对应的数据内容和一系列属性信息,同时也可以具有子节点。
zookeeper用于存储协调数据,如状态、配置、位置等信息,每个节点存储的数据量很小,KB级别。
在ZooKeeper中,ZNode可以分为持久节点和临时节点两类。
持久节点:指一旦这个ZNode被创建,除非主动进行ZNode的移除操作,否则这个ZNode将一直保存在ZooKeeper上。
临时节点:生命周期和客户端会话绑定,一旦客户端会话失效,这个客户端创建的所有临时节点都会被移除。
SEQUENTIAL:当用户为节点添加这个属性时,节点被创建时,ZooKeeper会自动在其节点后面追加一个整型数字,这个整型数字由父节点维护的自增数字。
版本 对于每个ZNode,ZooKeeper会为其维护一个Stat的数据结构,Stat中记录了Znode的三个数据版本,分别时version(当前Znode版本)、cversion(当前ZNode子节点的版本)和aversion(当前ZNode的ACL版本)。
Watcher Watcher(事件监听器),Zookeeper对Node的增删改查都可触发监听。
watch事件是一次性触发器,当watch监视的数据发生变化时,通知设置了该watch的client,即watcher。
watch事件异步发送至观察者。
watch是一次性出发的并且在获取watch事件和设置新watch事件之间又延迟,所以不能可靠的观察节点的每一次变化。
客户端监视一个节点总是先获取watch事件,再发现节点的数据变化。
watch事件的顺序对应于zookeeper服务所见的数据更新的顺序。
ACL ZooKeeper采用ACL(Access Control Lists)策略来进行权限控制,类似于UNIX文件系统的权限控制。ZooKeeper 5种权限:
CREATE:创建子节点的权限
READ:获取节点数据和子节点列表的权限
WRITE:更新节点数据的权限
DELETE:删除子节点的权限
ADMIN:设置节点ACL的权限
这5种权限简写为crwda(即:每个单词的首字符缩写)
**zookeeper的身份认证有4种方式 **
world:默认方式,相当于全世界都能访问
auth:代表已经认证通过的用户(cli中可以通过addauth digest user:pwd 来添加当前上下文中的授权用户)
digest:即用户名:密码这种方式认证,这也是业务系统中最常用的
ip:使用ip地址认证
ZAB协议 ZAB(ZooKeeper Atomic Broadcast,ZooKeeper原子消息广播协议)协议作为ZooKeeper数据一致性的核心算法。
ZAB协议是为分布式协调服务ZooKeeper专门设计的一种支持崩溃恢复的原子广播协议。给予该协议,ZooKeeper实现了一种主备模式的系统架构来保持集群中各副本之间数据的一致性。换言之,ZooKeeper使用一个单一的主进程来接收并处理客户端的所有事务请求,并采用ZAB的原子协议,将服务器数据的状态变更以事务Proposal的形式广播到所有的副本进程上去。ZAB协议的这个主备模型架构保证了同一时刻集群中只能够有一个主进程来广播服务器的状态变更,因此能够很好地处理客户端大量的并发请求。
ZAB协议核心:
所有事务请求必须由一个全局唯一的服务器来协调处理,即Leader服务器,余下其他服务器为Follower服务器。Leader服务器负责将一个客户端事务请求转换成一个事务Proposal(提议),并将该Proposal分发给集群中所有的Follower服务器。之后Leader服务器需要等待所有Follower服务器的反馈,一旦超过半数的Follower服务器进行正确的反馈后,那么Leader就会再次向所有的Follower服务器分发Commit消息,要求其将前一个Proposal进行提交。
ZooKeeper使用 部署 基本步骤 (1)下载并解压ZooKeeper至指定路径
下载路径
(2)配置zoo.cfg
将conf下 zoo_sample.cfg更名为zoo.cfg
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #客户端与服务器或者服务器与服务器之间心跳时间
service.N =H: A:B
N:代表服务器编号(也就是myid里面的值)
H:服务器地址
A:表示 Flower 跟 Leader的通信端口,简称服务端内部通信的端口(默认2888)
B:表示 是选举端口(默认是3888)
(3)创建myid文件
在dataDir所配置的目录下,创建名为myid的文件,在该文件的第一行写一个数字,和zoo.cfg中当前机器的编号对应上。
(4)启动服务器
bin/zkServer.sh start
(5)停止服务
bin/zkServer.sh stop
单机模式 zoo.cfg配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 tickTime=2000
伪集群模式 集群所有的机器都在一台机器上,只是以集群的特性来提供服务。
zoo.cfg配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 tickTime=2000
集群模式 集群模式和伪集群模式配置大体相同,唯一不同之处是集群的服务器分别运行在不同的机器上。
1 2 3 server.1=IP1:2888:3888
ZooKeeper命令 基本命令
脚本
说明
zkCleanup
清理ZooKeeper历史数据,包括事务日志文件和快照数据文件
zkCli
ZooKeeper的一个简易客户端
zkEnv
设置ZooKeeper的环境变量
zkServer
ZooKeeper服务器的启动、停止和重启脚本
客户端命令 通过zkCli.sh连接指定ZooKeeper服务器
zkCli.sh -server ip:port
create create [-s] [-e] path data acl
-s:顺序节点
-e:临时节点
例如: create -e /temp data1
ls 列出ZooKeeper指定节点下的所有子节点,也可以指定节点下第一级的所有子节点。
ls path [watch]
例如:ls /
get 获取ZooKeeper指定节点的数据内容和属性信息。
get path [watch]
例如:get /zk-book1
ls2 列出当前节点的子节点,同时列出节点状态
set 更新指定节点的数据内容。
set path data [version]
例如:set /temp data2 0
delete delete path [version]
此命令中的version参数和set命令中的version参数的作用是一致的。
h(help) 查看帮助
stat 查看节点的状态信息
在zookeeper中,每一次对节点的写操作都认为是一次事务,每一个事务,系统都会分配一个唯一的事务ID。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 czxid:节点被创建的事务ID ctime: 创建时间 mzxid: 最后一次被更新的事务ID mtime: 修改时间 0 dataLength:节点存储的数据的长度
rmr 递归删除节点(含子节点) 如:rmr /zk
setquota 设置配额,给节点限制值,比如限制子节点个数、节点数据的长度(当创建节点超出配额时,zookeeper不会抛出异常,会在zookeeper.out记录警告信息)
-n:限制子节点个数
listquota 查看配额,以及节点的配额状态
delquota 删除配额
close 关闭当前连接
history 查看历史执行指令
redo 重复执行指令
ACL相关 认证实例:
(1)增加一个认证用户
addauth digest 用户名:密码明文,如:addauth digest user1:password1
(2)设置权限:
setAcl /path auth:用户名:密码明文:权限,如:setAcl /test auth:user1:password1:cdrwa
setAcl /path digest:用户名:密码密文:权限
查看Acl设置:getAcl /path
Java客户端API使用 ZooKeeper客户端 会话创建 构造方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher);int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher,boolean canBeReadOnly);int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher,long sessionId, byte [] sessionPasswd);int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher,long sessionId, byte [] sessionPasswd, boolean canBeReadOnly)
参数说明:
参数名
说明
connectString
ZooKeeper服务器地址列表,由英文逗号分开的host:port字符串组成,每一个代表一台ZooKeeper服务器。例如192.168.1.2:2181,192.168.1.3:2181,192.168.1.4:2181
sessionTimeout
会话超时时间,“毫秒”级整型值。在会话周期内,ZooKeeper客户端和服务端通过心跳检测机制来维持会话的有效性,一旦在sessionTimeout时间内没有进行有效心跳检测,会话就会失效。
watcher
上面由Watcher介绍
canBeReadOnly
当前会话是否支持“read-only(只读)”模。
sessionId和sessionPasswd
分别代表会话ID和会话密钥。这两个参数能够确定一个会话,同时客户端使用这两个参数实现客户端会话复用,从而达到恢复会话效果。例子:第一次连接ZooKeeper服务器,然后调用ZooKeeper对象实例获取ID和密钥:long getSessionId();byte[] getSessionPasswd(); 下次创建ZooKeeper对象实例时候传入构造方法。
ZooKeeper客户端和服务端会话的建立时一个异步的过程,所以当初始化ZooKeeper构造方法完成时,不一定建立好了一个可用会话,此时会话的生命周期可能处于”CONNECTING”的状态。
创建ZooKeeper会话实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class ZooKeeperConstructorUsageSimple implements Watcher {private static CountDownLatch connectedSemaphore = new CountDownLatch (1 );public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {ZooKeeper zookeeper = new ZooKeeper (ZooKeeperConfig.HOST, 5000 , new ZooKeeperConstructorUsageSimple ());try {catch (InterruptedException e) {"ZooKeeper session established." );public void process (WatchedEvent event) {"Receive watched event:" + event);if (KeeperState.SyncConnected == event.getState()) {
打印信息:
1 2 3 CONNECTINGnull
创建复用sessionId和sessionPasswd的ZooKeeper会话实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class ZooKeeperConstructorUsageWithSIDPASSWD implements Watcher {private static CountDownLatch connectedSemaphore = new CountDownLatch (1 );public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ZooKeeper zookeeper = new ZooKeeper (ZooKeeperConfig.HOST, 5000 , new ZooKeeperConstructorUsageWithSIDPASSWD ());long sessionId = zookeeper.getSessionId();byte [] passwd = zookeeper.getSessionPasswd();new ZooKeeper (ZooKeeperConfig.HOST, 5000 , new ZooKeeper_Constructor_Usage_With_SID_PASSWD (),public void process (WatchedEvent event) {"Receive watched event:" + event);if (KeeperState.SyncConnected == event.getState()) {
创建节点 ZooKeeper不支持递归创建,即无法在父节点不存在的情况下创建一个子节点。当创建的节点已经存在时,会抛出NodeExistsException异常。
1 2 3 4 create (final String path, byte data[], List<ACL> acl, CreateMode createMode) void create (final String path, byte data[], List<ACL> acl, CreateMode createMode, StringCallback cb, Object ctx)
参数说明:
参数名
说明
path
需要创建的数据节点的节点路径,例如:/zk/book1
data
字节数组,节点创建后的初始内容
acl
节点ACL策略
createMode
节点类型,枚举类型:
cb
当服务端节点创建完毕后,ZooKeeper客户端会自动调用回调
ctx
用于传递一个对象,可以在回调方法执行的时候使用,通常时放一个上下文消息
ZooKeeper的节点内容只支持字节数组(byte[])类型,即ZooKeeper不负责为节点内容进行序列化,开发人员需要自己对节点内容进行序列化和反序列化。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;import org.apache.zookeeper.AsyncCallback;import org.apache.zookeeper.CreateMode;import org.apache.zookeeper.WatchedEvent;import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher;import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher.Event.KeeperState;import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooDefs.Ids;import com.newland.zookeeperdemo.ZooKeeperConfig;import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooKeeper;public class ZooKeeperCreateAPIUsage implements Watcher {private static CountDownLatch connectedSemaphore = new CountDownLatch (1 );public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ZooKeeper zookeeper = new ZooKeeper (ZooKeeperConfig.HOST, 5000 , new ZooKeeperCreateAPIUsage ());"/zk-test-ephemeral-" , "" .getBytes(), new IStringCallback (), "I am context." ); "/zk-test-ephemeral-" , "" .getBytes(), new IStringCallback (), "I am context." ); "/zk-test-ephemeral-" , "" .getBytes(), new IStringCallback (), "I am context." );String path1 = zookeeper.create("/zk-test-ephemeral-" , "" .getBytes(), "Success create znode: " + path1);String path2 = zookeeper.create("/zk-test-ephemeral-" , "" .getBytes(), "Success create znode: " + path2);public void process (WatchedEvent event) {if (KeeperState.SyncConnected == event.getState()) {class IStringCallback implements AsyncCallback .StringCallback{public void processResult (int rc, String path, Object ctx, String name) {"Create path result: [" + rc + ", " + path + ", " ", real path name: " + name);
打印信息:
异步信息
1 2 3 Create path result: [0 , /zk-test-ephemeral-, I am context., real path name: /zk-test-ephemeral-110 , /zk-test-ephemeral-, I am context., real path name: null 0 , /zk-test-ephemeral-, I am context., real path name: /zk-test-ephemeral-0000000002
同步信息
1 2 Success create znode: /zk-test-ephemeral-0000000007
AsyncCallback通知 StatCallback 节点状态异步通知回调
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 interface StatCallback extends AsyncCallback {public void processResult (int rc, String path, Object ctx, Stat stat) ;
DataCallback 此回调用于检索节点的数据和状态。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 interface DataCallback extends AsyncCallback {public void processResult (int rc, String path, Object ctx, byte data[], Stat stat) ;
ACLCallback 此回调用于检索节点的ACL和stat
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 interface ACLCallback extends AsyncCallback {public void processResult (int rc, String path, Object ctx, List<ACL> acl, Stat stat) ;
ChildrenCallback 此回调用于检索节点的子节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 interface ChildrenCallback extends AsyncCallback {public void processResult (int rc, String path, Object ctx, List<String> children) ;
Children2Callback 此回调用于检索节点的子节点和属性。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 interface Children2Callback extends AsyncCallback {public void processResult (int rc, String path, Object ctx, List<String> children, Stat stat) ;
StringCallback 创建节点异步接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 interface StringCallback extends AsyncCallback {public void processResult (int rc, String path, Object ctx, String name) ;
VoidCallback 这个回调不从节点检索任何东西 ,对于一些不希望返回任何内容的api是很有用的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 interface VoidCallback extends AsyncCallback {public void processResult (int rc, String path, Object ctx) ;
MultiCallback 此回调用于处理来自单个多调用的多个结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 interface MultiCallback extends AsyncCallback {public void processResult (int rc, String path, Object ctx, List<OpResult> opResults) ;
删除节点 只允许删除叶子节点。也就是说,如果一个节点存在至少一个叶子节点的话,那么该节点将无法被删除,必须先删除所有子节点。
1 2 void delete (final String path, int version) void delete (final String path, int version, VoidCallback cb, Object ctx)
例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class DeleteAPIUsage implements Watcher {private static CountDownLatch connectedSemaphore = new CountDownLatch (1 );private static ZooKeeper zk;public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {String path = "/zk-book" ;new ZooKeeper (ZooKeeperConfig.HOST, 5000 , new DeleteAPIUsage ());"" .getBytes(), Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL);1 );public void process (WatchedEvent event) {if (KeeperState.SyncConnected == event.getState()) {if (EventType.None == event.getType() && null == event.getPath()) {
打印信息:
读取数据 读取数据,包括子节点列表的获取和节点数据的获取。
getChildren 获取一个节点的所有子节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 List<String> getChildren (final String path, Watcher watcher) ;getChildren (String path, boolean watch) ;void getChildren (final String path, Watcher watcher, ChildrenCallback cb, Object ctx) ;void getChildren (String path, boolean watch, ChildrenCallback cb, Object ctx) ;getChildren (final String path, Watcher watcher,Stat stat) ;getChildren (String path, boolean watch, Stat stat) ;void getChildren (final String path, Watcher watcher, Children2Callback cb, Object ctx) ;void getChildren (String path, boolean watch, Children2Callback cb, Object ctx) ;
参数说明:
参数名
说明
path
指定数据节点路径
watcher
注册的Watcher,一旦在本次子节点获取之后,子节点列表发生变更就会向客户端发送通知。
watch
是否注册一个默认的Watcher
cb
异步回调
ctx
传递上下文信息对象
stat
指定数据节点的节点状态信息。在接口中传入一个旧的stat变量,该stat变量会在方法执行过程中,被来自服务端响应的新stat对象更新
如果ZooKeeper客户端获取到指定节点的子节点列表后,还需要订阅这个子节点列表的变化通知,可以注册一个Watcher。当子节点被添加或删除时,服务端就会向客户端发送一个NodeChildrenChanged(EventType.NodeChildrenChanged)类型的事件通知。但此时不包含最新的节点列表,客户端必须主动重新进行获取。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 import java.util.List;import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;import org.apache.zookeeper.AsyncCallback;import org.apache.zookeeper.CreateMode;import org.apache.zookeeper.WatchedEvent;import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher;import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher.Event.EventType;import org.apache.zookeeper.Watcher.Event.KeeperState;import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooDefs.Ids;import org.apache.zookeeper.ZooKeeper;import org.apache.zookeeper.data.Stat;import com.newland.zookeeperdemo.ZooKeeperConfig;public class ZooKeeper_GetChildren_API_ASync_Usage implements Watcher {private static CountDownLatch connectedSemaphore = new CountDownLatch (1 );private static ZooKeeper zk = null ;public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{String path = "/zk-book" ;new ZooKeeper (ZooKeeperConfig.HOST, 5000 , new ZooKeeper_GetChildren_API_ASync_Usage ());"" .getBytes(),Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.PERSISTENT);"/c1" , "" .getBytes(),Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL);true , new IChildren2Callback (), null );"/c2" , "" .getBytes(),Ids.OPEN_ACL_UNSAFE, CreateMode.EPHEMERAL);public void process (WatchedEvent event) {if (KeeperState.SyncConnected == event.getState()) {if (EventType.None == event.getType() && null == event.getPath()) {else if (event.getType() == EventType.NodeChildrenChanged) {try {"ReGet Child:" +zk.getChildren(event.getPath(),true ));catch (Exception e) {}class IChildren2Callback implements AsyncCallback .Children2Callback{public void processResult (int rc, String path, Object ctx, List<String> children, Stat stat) {"Get Children znode result: [response code: " + rc + ", param path: " + path", ctx: " + ctx + ", children list: " + children + ", stat: " + stat);
打印信息:
1 2 3 Get Children znode result: [response code: 0 , param path: /zk-book, ctx: null , children list: [c1], stat: 60 ,60 ,1550568158233 ,1550568158233 ,0 ,1 ,0 ,0 ,0 ,1 ,61
getData 获取节点数据内容
1 2 3 4 byte [] getData(final String path, Watcher watcher, Stat stat);byte [] getData(String path, boolean watch, Stat stat);void getData (final String path, Watcher watcher, DataCallback cb, Object ctx) ;void getData (String path, boolean watch, DataCallback cb, Object ctx) ;
参数说明:
参数名
说明
path
指定数据节点的节点路径
watcher
Watcher
stat
指定数据节点的节点状态信息
cb
数据获取回调
ctx
上下文对象
watch
是否注册默认Watcher
更新数据 更新操作时指定版本的数据版本进行的,当ZooKeeper服务器的版本与客户端携带的版本对的上时才更新数据。
1 2 Stat setData (final String path, byte data[], int version) ;void setData (final String path, byte data[], int version, StatCallback cb, Object ctx) ;
参数说明:
参数名
说明
path
指定路径
data[]
欲设值节点数据
version
当前节点数据版本
cb
数据节点的节点状态信息回调
ctx
上下文对象
检测节点是否存在 1 2 3 4 Stat exists (final String path, Watcher watcher) ;exists (String path, boolean watch) ;void exists (final String path, Watcher watcher, StatCallback cb, Object ctx) ;void exists (String path, boolean watch, StatCallback cb, Object ctx) ;
参数说明:
参数名
说明
path
指定数据节点节点路径
watcher
Watcher监听,节点创建、节点删除、节点更新
watch
是否复用ZooKeeper默认的Watcher
cb
异步回调
ctx
用于传递上下文信息的对象
权限控制 ZooKeeper提供ACL的权限控制机制,通过设置ZooKeeper服务器上数据节点的ACL来控制客户端对该数据节点的访问权限。
ZooKeeper提供多种权限控制模式,分别是world、auth、digest、ip和super。
在完成ZooKeeper会话创建后,给该会话添加权限信息(AuthInfo)
1 void addAuthInfo (String scheme, byte auth[])
参数说明:
参数名
说明
scheme
权限控制模式,分别时world、auth、digest、ip和super。
auth
具體的权限信息
该接口主要用于当前ZooKeeper会话添加权限信息,但凡通过该会话对ZooKeeper服务器进行的任何操作,都会带上该权限信息。
1 2 ZooKeeper zookeeper = new ZooKeeper (ZooKeeperConfig.HOST,50000 ,null );"digest" , "foo:true" .getBytes());
ZkClient 1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > com.101tec</groupId > <artifactId > zkclient</artifactId > <version > 0.11</version > </dependency >
会话创建 ZkClient对ZooKeeper进行了封装,从API级别来支持Watcher监听的注册。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ZkClient(String serverstring) ;int connectionTimeout);int sessionTimeout, int connectionTimeout);int sessionTimeout,int connectionTimeout,ZkSerializer zkSerializer) ;final String zkServers, final int sessionTimeout, final int connectionTimeout, final ZkSerializer zkSerializer, final long operationRetryTimeout);int connectionTimeout);int connectionTimeout, ZkSerializer zkSerializer);final IZkConnection zkConnection, final int connectionTimeout, final ZkSerializer zkSerializer, final long operationRetryTimeout);
参数说明
参数名
说明
zkServers
ZooKeeper服务器列表
sessionTimeout
会话超时时间,毫秒级单位
connectionTimeout
连接创建超时时间,毫秒级单位
connection
IZKConnection接口实现类
zkSerializer
自定义序列化器
例如:
1 ZkClient zkClient = new ZkClient (ZooKeeperConfig.HOST, 15000 );
创建节点 1 2 3 4 String create (final String path, byte data[], List<ACL> acl, CreateMode createMode)void create (final String path, byte data[], List<ACL> acl, CreateMode createMode, StringCallback cb, Object ctx)
参数
说明
path
节点路径
data
节点的初始数据内容,可以传入null
mode
节点类型,枚举类型。
acl
ACL策略
callback
异步回调函数
context
上下文对象
createParents
是否创建父节点,ZkClient可以递归创建父节点
1 2 3 4 ZkClient zkClient = new ZkClient (ZooKeeperConfig.HOST, 15000 );String path = "/zk-book/c1" ;true );
删除节点 1 2 void delete (final String path, int version) void delete (final String path, int version, VoidCallback cb, Object ctx)
deleteRecursive可以自动完成遍历删除节点。
1 2 3 String path = "/zk-book" ;ZkClient zkClient = new ZkClient (com.newland.zookeeperdemo.ZooKeeperConfig.HOST, 2000 );
读取数据 getChildren 获取所有的子节点
1 List<String> getChildren (String path)
IZkChildListener用来监听子节点的变化(新增子节点、删除子节点、删除节点):
1 2 3 4 5 zkClient.subscribeChildChanges(path, new IZkChildListener () {public void handleChildChange (String parentPath, List<String> currentChilds) throws Exception {" 's child changed, currentChilds:" + currentChilds);
字段
说明
parentPath
父节点路径
currentChilds
子节点列表
readData 1 2 3 4 byte [] getData(final String path, Watcher watcher, Stat stat);byte [] getData(String path, boolean watch, Stat stat);void getData (final String path, Watcher watcher, DataCallback cb, Object ctx) ;void getData (String path, boolean watch, DataCallback cb, Object ctx) ;
更新数据 1 2 Stat setData (final String path, byte data[], int version) ;void setData (final String path, byte data[], int version, StatCallback cb, Object ctx) ;
expectedVersion: 预期的数据版本
通過IZkDataListener可以监听数据变化(节点数据变化、删除节点):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 zkClient.subscribeDataChanges(path, new IZkDataListener () {public void handleDataDeleted (String dataPath) throws Exception {"Node " + dataPath + " deleted." );public void handleDataChange (String dataPath, Object data) throws Exception {"Node " + dataPath + " changed, new data: " + data);
字段
说明
dataPath
数据节点路径
data
节点对应数据
检测节点是否存在 1 2 3 4 Stat exists (final String path, Watcher watcher) ;exists (String path, boolean watch) ;void exists (final String path, Watcher watcher, StatCallback cb, Object ctx) ;void exists (String path, boolean watch, StatCallback cb, Object ctx) ;
Curator 1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.curator</groupId > <artifactId > curator-framework</artifactId > <version > 2.4.2</version > </dependency >
创建会话 创建会话使用的是CuratorFrameworkFactory.Builder
1 2 static CuratorFramework newClient (String connectString, RetryPolicy retryPolicy) ;static CuratorFramework newClient (String connectString, int sessionTimeoutMs, int connectionTimeoutMs, RetryPolicy retryPolicy) ;
但其内部还是采用的build模式,使用的是CuratorFrameworkFactory.Builder
参数
说明
connectString
服务器地址,通过逗号进行连接
sessionTimeoutMs
会话超时时间,毫秒单位
connectionTimeoutMs
连接超时时间,毫秒单位
retryPolicy
重试策略。四种:ExponentialBackoffRetry、RetryNTimes、RetryOneTime、RetryUnitlElapsed
实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 CuratorFramework client = 5000 ,3000 ,
build方式创建:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 RetryPolicy retryPolicy = new ExponentialBackoffRetry (1000 , 3 );CuratorFramework client = 5000 )
builder可以指定如/base的独立命名空间,客户端对ZooKeeper上数据节点的任何操作,都是基于该相对目录进行的。
1 CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder ().namespace ("base" )
重试策略 ExponentialBackoffRetry 1 2 ExponentialBackoffRetry(int baseSleepTimeMs, int maxRetries);int baseSleepTimeMs, int maxRetries, int maxSleepMs);
参数
说明
baseSleepTimeMs
初始sleep时间
maxRetries
最大重试次数
maxSleepMs
最大sleep时间
ExponentialBackoffRetry设计:
当前sleep时间=baseSleepTimeMs*Math.max(1,random.nextInt(1<<(retryCount+1)))
随着重试次数的增加,计算出的sleep时间会越来也大。
最后必须限制在maxSleepMs时间内,即sleep=Math.min(sleep,maxSleepMs)
自定义重试策略 通过实现RetryPolicy可以自定义重试策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public interface RetryPolicy {public boolean allowRetry (int retryCount, long elapsedTimeMs, RetrySleeper sleeper) ;
创建节点 1 2 3 4 client.create()"init" .getBytes());
如果没有设置节点属性,那么Curator默认创建的持久节点,内容默认是空。
creatingParentsIfNeeded():如果父节点不存在,自动递归创建临时节点。
删除节点 1 2 3 4 Stat stat = new Stat ();
deletingChildrenIfNeeded()删除一个节点,并递归删除其所有子节点。
读取数据 1 2 Stat stat = new Stat ();byte [] buffer = client.getData().storingStatIn(stat).forPath(path);
storingStatIn通过传入一个旧的stat的方式来存储服务器返回的最新的节点状态。
更新数据 1 client.setData().withVersion(stat.getVersion()).forPath(path,"newdata" .getBytes());
当stat变量的版本过期时,会抛出KeeperErrorCode=BadVersion。
异步处理 BackgroundCallback:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public interface BackgroundCallback {public void processResult (CuratorFramework client, CuratorEvent event) throws Exception;
事件类型(CuratorEventType)
CuratorEvent的getType()返回值代表本次事件的类型,主要有CREATE、DELETE、EXISTS、GET_DATA、SET_DATA、CHILDREN、SYNC、GET_ACL、WATCHED和CLOSING,分别代表Curator Framework#create()、CuratorFramework#getData、CuratorFramework#setData()、CuratorFramework#getChildren()、CuratorFramework#sync(String,Object)、CuratorFramework#getACL()、Watchable#using Watcher(Watcher)/Watchab le#watched()和ZooKeeper客户端与服务端连接断开事件。
响应码(int)
0(ok)、-4(ConnectionLoss)、-110(NodeExists)和-112(SessionExpired)等,分别代表调用成功、客户端与服务端已断开、指定节点已存在和会话已过期等。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 client.create().creatingParentsIfNeeded().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL).inBackground(new BackgroundCallback () {public void processResult (CuratorFramework client, CuratorEvent event) throws Exception {"event[code: " + event.getResultCode() + ", type: " + event.getType() + "]" );"Thread of processResult: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());"init" .getBytes());
Curator典型使用 1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.curator</groupId > <artifactId > curator-recipes</artifactId > <version > 2.4.2</version > </dependency >
事件监听 ZooKeeper原生支持通过注册Watcher来进行事件监听,但是其使用并不是特别方便,需要反复注册Watcher,比较繁琐。Curator引入Cache来实现对ZooKeeper服务端事件的监听。Cache是Curator中对事件监听的包装,其对事件的监听可看作是一个本地缓存试图和远程ZooKeeper视图的对比过程。同时Curator能够自动为开发人员反复注册监听,从而大大简化了原声API开发的繁琐过程。Cache分为两类监听类型:节点监听和子节点监听。
NodeCache:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public NodeCache (CuratorFramework client, String path) ;public NodeCache (CuratorFramework client, String path, boolean dataIsCompressed) ;
NodeCacheListener接口是当节点内容发生变化的时候,就会回调方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 final NodeCache cache = new NodeCache (client, path, false );true );new NodeCacheListener () {public void nodeChanged () throws Exception {"Node data update, new data: " + new String (cache.getCurrentData().getData()));"u" .getBytes());
控制台:
1 Node data update, new data : u
如果原节点不存在,Cache就会在节点被创建后触发NodeCacheListener;但如果该数据节点被删除,那么Curator就无法触发NodeCacheListener。
PathChildrenCache:
用于监听指定ZooKeeper数据节点的子节点变化情况。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public PathChildrenCache (CuratorFramework client, String path, boolean cacheData, boolean dataIsCompressed, final CloseableExecutorService executorService) ;
PathChildrenCache还有其它构造方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public interface PathChildrenCacheListener {public void childEvent (CuratorFramework client, PathChildrenCacheEvent event) throws Exception;
当指定节点的子节点发生变化时,就会回调该方法。PathChildrenCacheEvent类中定义了所有的事件类型,包括新增子节点(CHILD_ADDED)、子节点数据变更(CHILD_UPDATED)和子节点删除(CHILD_REMOVED)三类。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 PathChildrenCache cache = new PathChildrenCache (client, path, true );new PathChildrenCacheListener () {public void childEvent (CuratorFramework client, PathChildrenCacheEvent event) throws Exception {switch (event.getType()) {case CHILD_ADDED:"CHILD_ADDED," + event.getData().getPath());break ;case CHILD_UPDATED:"CHILD_UPDATED," + event.getData().getPath());break ;case CHILD_REMOVED:"CHILD_REMOVED," + event.getData().getPath());break ;default :break ;1000 );"/c1" );1000 );"/c1" );1000 );
Master选举 考虑7*24小时向外提供服务的系统,不能有单点故障,于是我们使用集群,采用的是Master+Slave。集群中有一台主机和多台备机,由主机向外提供服务,备机监听主机状态,一旦主机宕机,备机必需迅速接管主机继续向外提供服务。在这个过程中,从备机选出一台机作为主机的过程,就是Master选举。
zookeeper典型应用场景之一:master选举
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 LeaderSelector selector = new LeaderSelector (client, master_path, new LeaderSelectorListenerAdapter () {public void takeLeadership (CuratorFramework client) throws Exception {"成为Master角色" );3000 );"完成Master操作,释放Master权利" );
当多个应用进行选举时,一个应用程序完成Master逻辑后,另一个应用程序的takeLeadership方法才会被调用。这说明,当一个应用实例完成Master选举后,其它应用实例会进入等待,知道当前Master挂了或退出后才会开始选举新的Master。
当进行选举时,master_path节点下回创建一个后缀时数字,且不断增加的节点
1 _c_1288f3b3-88b8 -4f45-925c-1a173ac0be54-lock-0000000277
分布式锁 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 final InterProcessMutex lock = new InterProcessMutex (client,lock_path);final CountDownLatch down = new CountDownLatch (1 );for (int i = 0 ; i < 30 ; i++){new Thread (new Runnable () {public void run () {try {catch ( Exception e ) {}SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat ("HH:mm:ss|SSS" );String orderNo = sdf.format(new Date ());"生成的订单号是 : " +orderNo);try {catch ( Exception e ) {}
分布式计数器 DistributedAtomicInteger时分布式环境中使用的原子整形。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 DistributedAtomicInteger atomicInteger = new DistributedAtomicInteger (client, distatomicint_path, new RetryNTimes ( 3 , 1000 ));8 );"Result: " + rc.succeeded()+" " +rc.preValue()+" " +rc.postValue() );"Result: " + rc.succeeded()+" " +atomicValue.preValue()+" " +atomicValue.postValue() );
分布式Barrier Barrier是一种用来控制多线程之前同步的,在JDK中自带了CyclicBarrier实现。
JDK的实例查看Recipes_CyclicBarrier
ZK实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Recipes_Barrier {static String barrier_path = "/curator_recipes_barrier_path" ;static DistributedBarrier barrier;public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {for (int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) {new Thread (new Runnable () {public void run () {try {CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()new ExponentialBackoffRetry (1000 , 3 )).build();new DistributedBarrier (client, barrier_path);"号barrier设置" );"启动..." );catch (Exception e) {}12000 );
上面开启了5个线程,通过调用DistributedBarrier.setBarrier()方法完成Barrier的设置,并通过调用waitOnBarrier()方法来等待Barrier的释放。然后调用DistributedBarrier.removeBarrier()释放Barrier,同时触发所有等待该Barrier的5个线程继续执行。
另一种方式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder() .connectString(com.newland.zookeeperdemo.ZooKeeperConfig.HOST)new ExponentialBackoffRetry (1000 , 3 )).build();DistributedDoubleBarrier barrier = new DistributedDoubleBarrier (client, barrier_path,5 );3000 ) );"号进入barrier" );"启动..." );3000 ) );"退出..." );
每个Barrier的参与者都会在调用DistributedDoubleBarrier.enter()方法之后进行等待,此时处于准备进入状态。一旦准备进入Barrier的成员数达到5个后,所有的成员会被同时触发进入。之后调用DistributedDoubleBarrier.leave()方法则会再次等待,此时处于准备退出状态。一旦准备退出Barrier的成员数达到5个后,所有的成员同样会被同时触发退出。因此DistributedDoubleBarrier能够控制同时进入和退出。
Curator工具 ZKPaths ZKPaths提供了一些简单的API来构建ZNode路径、递归创建和删除节点等。http://curator.apache.org/apidocs/org/apache/curator/utils/ZKPaths.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {String path = "/curator_zkpath_sample" ;ZooKeeper zookeeper = client.getZookeeperClient().getZooKeeper();"sub" ));"sub" ));"/curator_zkpath_sample/sub1" ) );PathAndNode pn = ZKPaths.getPathAndNode( "/curator_zkpath_sample/sub1" );String dir1 = path + "/child1" ;String dir2 = path + "/child2" ;true );
打印:
1 2 3 4 5 6 /curator_zkpath_sample/ sub/curator_zkpath_sample/ sub
EnsurePath EnsurePath提供了一种能够确保数据节点存在的机制,它采取了静默的节点创建方式,其内部实现就是试图创建指定节点,如果节点已经存在,那么就不进行任何操作,也不对外抛出异常,否则正常创建数据节点。
http://curator.apache.org/apidocs/org/apache/curator/utils/EnsurePath.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { "zk-book" );EnsurePath ensurePath = new EnsurePath (path);EnsurePath ensurePath2 = client.newNamespaceAwareEnsurePath("/c1" );
TestingServer TestingServer允许开发人员非常方便启动一个标准的ZooKeeper服务器,并以此来进行一系列的单元测试。需要引入:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.curator</groupId > <artifactId > curator-test</artifactId > <version > 2.4.2</version > </dependency >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {TestingServer server = new TestingServer (2181 ,new File ("/home/admin/zk-book-data" ));CuratorFramework client = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder()5000 )new ExponentialBackoffRetry (1000 , 3 ))String path = "/zookeeper" ;
TestingCluster Curator提供启动ZooKeeper集群的工具类,可以模拟ZooKeeper集群环境的Curator工具类,能够便于开发人员在本地模拟由n台机器组成的集群环境。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {TestingCluster cluster = new TestingCluster (3 );2000 );TestingZooKeeperServer leader = null ;for (TestingZooKeeperServer zs : cluster.getServers()){"-" );"-" ); if ( zs.getQuorumPeer().getServerState().equals( "leading" )){"--After leader kill:" );for (TestingZooKeeperServer zs : cluster.getServers()){"-" );"-" );
ZooKeeper典型应用场景 ZooKeeper是一个典型的发布/订阅模式的分布式数据管理与协调框架,可以使用他来进行分布式数据的发布与订阅。另外,通过对ZooKeeper中丰富的数据节点类型进行交叉使用,配合Watcher事件通知机制,可以非常方便地构建一系列分布式应用中都会设计的核心功能,如数据发布/订阅、负载均衡、命名服务、分布式协调/通知、集群管理、Master选举、分布式锁和分布式队列等。
数据发布/订阅 数据发布/订阅系统,即所谓的配置中心,就是发布者将数据发布到ZooKeeper的一个或一系列节点上,供订阅者进行数据订阅,进而达到动态获取数据的目的,实现配置信息的集中式管理和数据的动态更新。
负载均衡 负载均衡是一种相当常见的计算机网络技术,用来对多个计算机(计算机集群)、网络连接、CPU、磁盘驱动器或其他资源进行分配负载,已达到优化均衡使用、最大化吞吐率、最小化响应时间和避免过载的目的。
分布式协调/通知 将不同的分布式组件有机结合起来的关键所在。对于一个在多台机器上部署运行的应用而言,通常需要一个协调者来控制整个系统的运行流程,例如分布式事务的处理、机器间的互相协调等 。同时,引入这样一个协调者,便于将分布式协调的职责从应用中分离出来,从而大大减少系统之间的耦合性,而且能够显著提高系统的可扩展性。
分布式锁 分布式锁是控制分布式系统之间同步访问共享资源的一种方式。
排他锁 又称独占所
定义锁 两种常见方式可以用来定义锁,分别是synchronized机制和JDK5提供的ReentrantLock。而Zookeeper是通过ZooKeeper上的数据节点来表示一个锁,例如/exclusive_lock/lock节点就可以定义为一个锁。
获取锁 在需要获取排他锁时,所有的客户端都会试图通过调用create()接口,在/exclusive_lock节点下创建临时子节点/exclusive_lock/lock。如果创建成功,就获取了锁。同时所有获取到锁的客户端就需要到/exclusive_lock节点上注册一个子节点变更的 Watcher监听,以便实时监听到lock节点的变更情况。
释放锁 /exclusive_lock/lock是一个临时节点,下面两种情况可能释放锁:
(1)当获取锁的客户端机器宕机,临时节点就会被移除。
(2)正常执行完业务逻辑后,客户端就会主动将自己创建的临时节点删除。
当等待所的客户端接到通知后,会再次发起分布式锁获取。
共享锁 又称读锁。
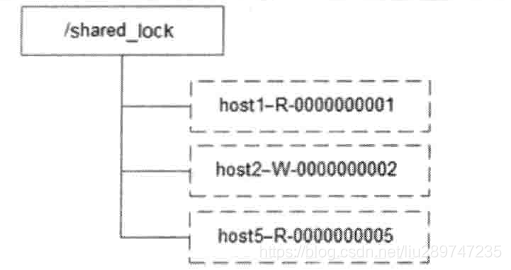
定义所 同样通过ZooKeeper上的数据节点来表示一个锁,是一个类似于”/shared_lock/[hostname]-请求类型-序号”的临时顺序节点。
获取锁 在需要获取共享锁时,所有客户端都会到/shared_lock这个节点下面创建一个临时顺序节点,如果当前是读请求,那么创建例如/shared_lock/192.168.1.1-R-00000001的节点;如果是写请求,那么创建例如/shared_lock/192.168.1.1-W-00000001节点。
判断读写顺序 根据共享锁的定义,不同的事务都可以同时对同一个对象数据进行读取操作,而更新操作必须在当前没有任何事务进行读写操作的情况下进行。
步骤:
(1)创建完节点后,获取/shared_lock节点的所有子节点,并对该节点注册子节点变更的Watcher监听。
(2)确定自己的节点序号在所有子节点的顺序
(3)对于读请求:
对鞋写请求:
(4)接收到Watcher通知后,重复步骤(1).
改进分布式锁实现 为了避免上面ZooKeeper分布式锁羊群效应,对分布式锁做以下改进:
(1)客户端调用create()方法创建一个类似于“/shared_lock/[hostname]-请求类型-序号”的临时顺序节点。
分布式队列 FIFO:先入先出 创建临时顺序节点来实现
Barrier(分布式屏障) 例如n=10表示只有当/queue_barrier节点下的子节点个数达到10后,才会打开Barrier。之后,所有的客户端都会在/queue_barrier节点下创建一个临时节点,例如/queue_barrier/192.168.1.1。
zookeeper在大型分布式系统中的应用 https://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/p/6063694.htm
参考资料: